Cluster Types
Terminology
An N-node cluster is a Dgraph cluster that contains N number of Dgraph instances. For example, a 6-node cluster means six Dgraph instances. The replication setting specifies the number of Dgraph Alpha replicas that are in each group. If this is higher than 1, each alpha in a group will hold a full copy of that group’s data. The replication setting is a configuration flag (--replicas) on Dgraph Zero. Sharding is done (typically for databases near 1TB in size) by creating multiple Dgraph Alpha groups. Every Dgraph Alpha group is automatically assigned a set of distinct predicates to store and serve, thus dividing up the data.
Examples of different cluster settings:
- No sharding
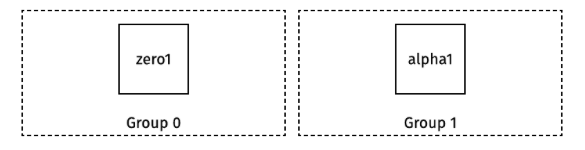
- 2-node cluster: 1 Zero, 1 Alpha (one group).
- HA equivalent: x3 = 6-node cluster.
- With 2-way sharding:
- 3-node cluster: 1 Zero, 2 Alphas (two groups).
- HA equivalent: x3 = 9-node cluster.
In the following examples we outline the two most common cluster configurations: a 2-node cluster and a 6-node cluster.
Basic setup: 2-node cluster
We provide sample configs for both Docker Compose and Kubernetes for a 2-node cluster. You can also run Dgraph directly on your host machines.
Configuration can be set either as command-line flags, environment variables, or in a config file (see Config).
Dgraph Zero:
- The
--myflag should be set to the address:port (the internal-gRPC port) that will be accessible to the Dgraph Alpha (default:localhost:5080). - The
--raftsuperflag’sidxoption should be set to a unique Raft ID within the Dgraph Zero group (default:1). - The
--walflag should be set to the directory path to store write-ahead-log entries on disk (default:zw). - The
--bindallflag should be set to true for machine-to-machine communication (default:true). - Recommended: For better issue diagnostics, set the log level verbosity to 2 with the option
--v=2.
Dgraph Alpha:
- The
--myflag should be set to the address:port (the internal-gRPC port) that will be accessible to the Dgraph Zero (default:localhost:7080). - The
--zeroflag should be set to the corresponding Zero address set for Dgraph Zero’s--myflag. - The
--postingsflag should be set to the directory path for data storage (default:p). - The
--walflag should be set to the directory path for write-ahead-log entries (default:w) - The
--bindallflag should be set to true for machine-to-machine communication (default:true). - Recommended: For better issue diagnostics, set the log level verbosity to 2
--v=2.
HA setup: 6-node cluster
We provide sample configs for both Docker Compose and Kubernetes for a 6-node cluster with 3 Alpha replicas per group. You can also run Dgraph directly on your host machines.
A Dgraph cluster can be configured in a high-availability setup with Dgraph Zero and Dgraph Alpha each set up with peers. These peers are part of Raft consensus groups, which elect a single leader among themselves. The non-leader peers are called followers. In the event that the peers cannot communicate with the leader (e.g., a network partition or a machine shuts down), the group automatically elects a new leader to continue.
Configuration can be set either as command-line flags, environment variables, or in a config file (see Config).
In this setup, we assume the following hostnames are set:
zero1zero2zero3alpha1alpha2alpha3
We will configure the cluster with 3 Alpha replicas per group. The cluster group-membership topology will look like the following:
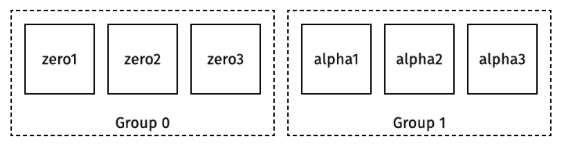
Set up Dgraph Zero group
In the Dgraph Zero group you must set unique Raft IDs (--raft superflag’s idx option) per Dgraph Zero. Dgraph will not auto-assign Raft IDs to Dgraph Zero instances.
The first Dgraph Zero that starts will initiate the database cluster. Any following Dgraph Zero instances must connect to the cluster via the --peer flag to join. If the --peer flag is omitted from the peers, then the Dgraph Zero will create its own independent Dgraph cluster.
First Dgraph Zero example: dgraph zero --replicas=3 --raft idx=1 --my=zero1:5080
The --my flag must be set to the address:port of this instance that peers will connect to. The --raft superflag’s idx option sets its Raft ID to 1.
Second Dgraph Zero example: dgraph zero --replicas=3 --raft idx=2 --my=zero2:5080 --peer=zero1:5080
The --my flag must be set to the address:port of this instance that peers will connect to. The --raft superflag’s idx option sets its Raft ID to 2, and the --peer flag specifies a request to connect to the Dgraph cluster of zero1 instead of initializing a new one.
Third Dgraph Zero example: dgraph zero --replicas=3 --raft idx=3 --my=zero3:5080 --peer=zero1:5080:
The --my flag must be set to the address:port of this instance that peers will connect to. The --raft superflag’s idx option sets its Raft ID to 3, and the --peer flag specifies a request to connect to the Dgraph cluster of zero1 instead of initializing a new one.
Dgraph Zero configuration options:
- The
--myflag should be set to the address:port (the internal-gRPC port) that will be accessible to Dgraph Alpha (default:localhost:5080). - The
--raftsuperflag’sidxoption should be set to a unique Raft ID within the Dgraph Zero group (default:1). - The
--walflag should be set to the directory path to store write-ahead-log entries on disk (default:zw). - The
--bindallflag should be set to true for machine-to-machine communication (default:true). - Recommended: For more informative log info, set the log level verbosity to 2 with the option
--v=2.
Set up Dgraph Alpha group
The number of replica members per Alpha group depends on the setting of Dgraph Zero’s --replicas flag. Above, it is set to 3. So when Dgraph Alphas join the cluster, Dgraph Zero will assign it to an Alpha group to fill in its members up to the limit per group set by the --replicas flag.
First Alpha example: dgraph alpha --my=alpha1:7080 --zero=zero1:5080
Second Alpha example: dgraph alpha --my=alpha2:7080 --zero=zero1:5080
Third Alpha example: dgraph alpha --my=alpha3:7080 --zero=zero1:5080
Dgraph Alpha configuration options:
- The
--myflag should be set to the address:port (the internal-gRPC port) that will be accessible to the Dgraph Zero (default:localhost:7080). - The
--zeroflag should be set to the corresponding Zero address set for Dgraph Zero’s--myflag. - The
--postingsflag should be set to the directory path for data storage (default:p). - The
--walflag should be set to the directory path for write-ahead-log entries (default:w) - The
--bindallflag should be set to true for machine-to-machine communication (default:true). - Recommended: For more informative log info, set the log level verbosity to 2
--v=2.